After publishing our video on Camotes we received a lot of questions about eating sweet potato greens and their various health benefits.
 What’s The Big Deal, Just Another Green right?
What’s The Big Deal, Just Another Green right?
No……these guys are far more than just a salad topper. I dug and little deeper into sweet potato greens (Ipomoea batatas) and found an interesting study on their effect on prostate cancer cells and how certain polyphenol compounds play a role. Coincidentally, sweet potato greens are an excellent (if not the best) source of dietary polyphenols such as anthocyanins and phenolic acids. They’re also one of our favorite greens here at the house. Polyphenols are a type of chemical that act as antioxidants and protect cells against damage caused by free radicals. These are often associated with anti aging effects and aiding other health problems related to oxidative stress.
Here are some of the ways that sweet potato greens may help to fight cancer:
- Inhibiting tumor growth: Sweet potato greens contain compounds that can inhibit the growth of cancer cells. One study found that sweet potato greens extract was able to inhibit the growth of prostate cancer cells in mice.
- Inducing apoptosis: Apoptosis is a process of programmed cell death. Sweet potato greens extract has been shown to induce apoptosis in cancer cells. This means that sweet potato greens may help to kill cancer cells.
- Preventing metastasis: Metastasis is the process by which cancer cells spread to other parts of the body. Sweet potato greens extract has been shown to prevent the metastasis of cancer cells in mice.
- Protecting against DNA damage: DNA damage is thought to play a role in the development of cancer. Sweet potato greens contain antioxidants that can help to protect the body from DNA damage.
According to the Extension Service at the University of Arkansas
Sweet potato leaves represent at least 15 anthocyanin and 6 polyphenolic compounds. These biologically active compounds possess multifaceted action, including antioxidation, antimutagenicity, antiinflammation and anticarcinogenesis. Sweet potato leaves contain more total polyphenols than any other commercial vegetables, including sweetpotato roots and potato tubers.
That’s right…more total polyphenols than ANY commercially available vegetable.
Prostate Cancer and Sweet Potato Green Extract (SPGE)
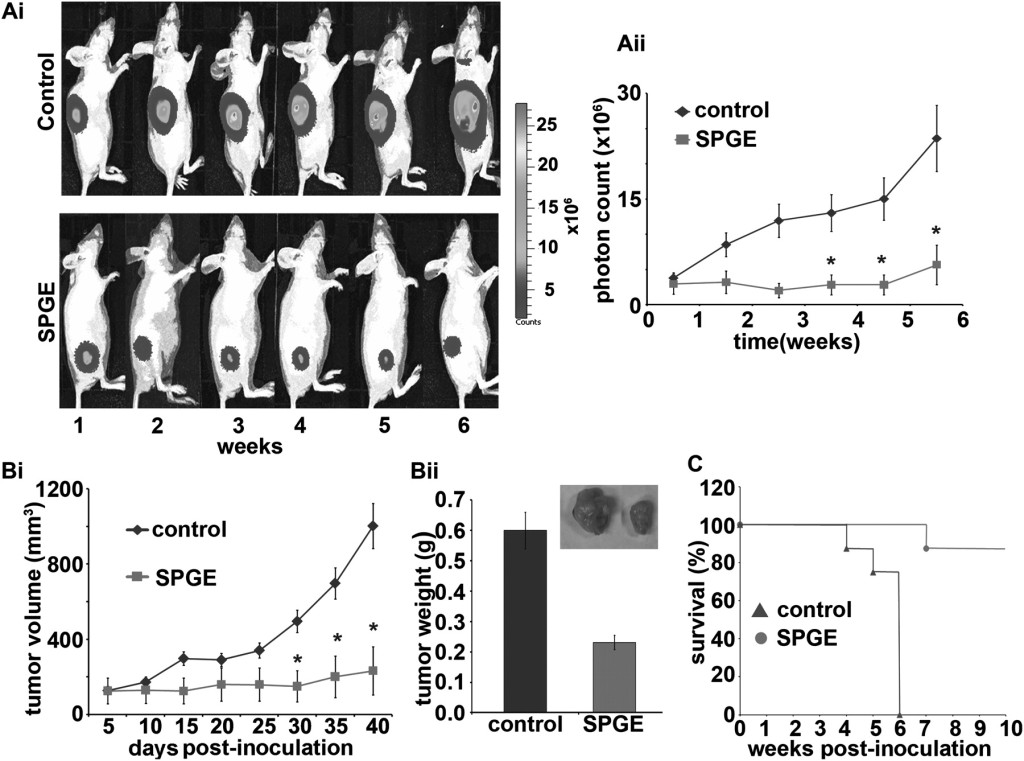
In a 2011 study, it was found that an extract of sweet potato is extremely toxic to cells of prostate cancer, killing 94% of them in vitro and produces a slowdown in the growth of prostate tumors in mice by 75%.
Oral administration of 400 mg/kg SPGE remarkably inhibited growth and progression of prostate tumor xenografts by ?69% in nude mice, as shown by tumor volume measurements and non-invasive real-time bioluminescent imaging. Most importantly, SPGE did not cause any detectable toxicity to rapidly dividing normal tissues such as gut and bone marrow. This is the first report to demonstrate the in vitro and in vivo anticancer activity of sweet potato greens in prostate cancer.
I’m not an oncologist, and realize studies like this need to be repeatable and subjected to peer review. However, this is compelling evidence for further evaluation of sweet potato green extract as a regimen against prostate cancer. Below are some of the results from the in vivo part of the study.
Other Studies on Sweet Potato Greens
Other research has shown that these leaves are also active against other forms of cancer. A study in Taiwan showed that were associated with the reduced risk for lung cancer.
In another study, purple sweet potato leaves were shown to boost immune system response in humans. Specifically it showed a significant increase in proliferation responsiveness of peripheral blood mononuclear cells. These PBMC’s cells include lymphocytes (T cells, B cells, and NK, or “killer” cells) which are the heavy hitters in our body’s immune system.
 But, why waste time with cancer when we can tackle diabetes? This study showed sweet potato greens to lower blood glucose levels in mice with type II diabetes. According to the authors of the study, the sweet potato leaves contain polyphenols such as caffeoylquinic acid (CQA) derivatives. It has multiple biological functions and may help to regulate the blood glucose concentration.
But, why waste time with cancer when we can tackle diabetes? This study showed sweet potato greens to lower blood glucose levels in mice with type II diabetes. According to the authors of the study, the sweet potato leaves contain polyphenols such as caffeoylquinic acid (CQA) derivatives. It has multiple biological functions and may help to regulate the blood glucose concentration.
Herbal Shotgun Approach
The thing that’s interesting about these studies is that they’re not using the conventional ‘silver bullet’ method popular in modern medicine. They use whole plant extracts instead of isolating one chemical and testing with it. In other studies, I’ve seen this described as the “herbal shotgun” or “synergistic multi-target effects” approach. It makes sense. Millions of years of evolution have built biological systems that utilize chemicals in multiple channels and in varied ways. Maybe we can build on nature’s “shotgun” biology by doing more studies with whole plants and concentrates. The big plus here is, if more studies can confirm effective treatments using whole plant extracts, therapy could become more available and much cheaper. In the case of sweet potato leaves, it might just involve adding them to your daily diet.
How to eat sweet potato greens
Sweet potato greens can be eaten raw, cooked, or dried. The leaves can be added to salads, sandwiches, and stir-fries. They can also be cooked and eaten as a side dish.
Here are some tips for preparing sweet potato greens:
- Wash the leaves thoroughly before eating them.
- Remove the stems from the leaves before cooking them.
- Steam or sauté the leaves for a few minutes until they are tender.
- Season the leaves with salt, pepper, and other herbs and spices to taste.
Sources:
Nutritional and Medicinal Qualities of Sweetpotato Tops and Leaves– University of Arkansas




GIPHY App Key not set. Please check settings
One Comment